Integumentary System
Shyam Sunder , 19-Nov-2025
Integumentary System
The integumentary system includes the skin, hair, nails, sebaceous glands and sweat glands.
Specialty Dermatology • Physician Dermatologist
Structure of Skin
The skin is divided into two primary layers:
- Epidermis
- The outer layer of skin.
- Dermis
- The inner layer of skin.
Functions
- Protecting internal organs against infection, injuries and harmful chemicals.
- Maintaining body temperature.
- Synthesizing vitamin D when exposed to sunlight.
Skin lesions
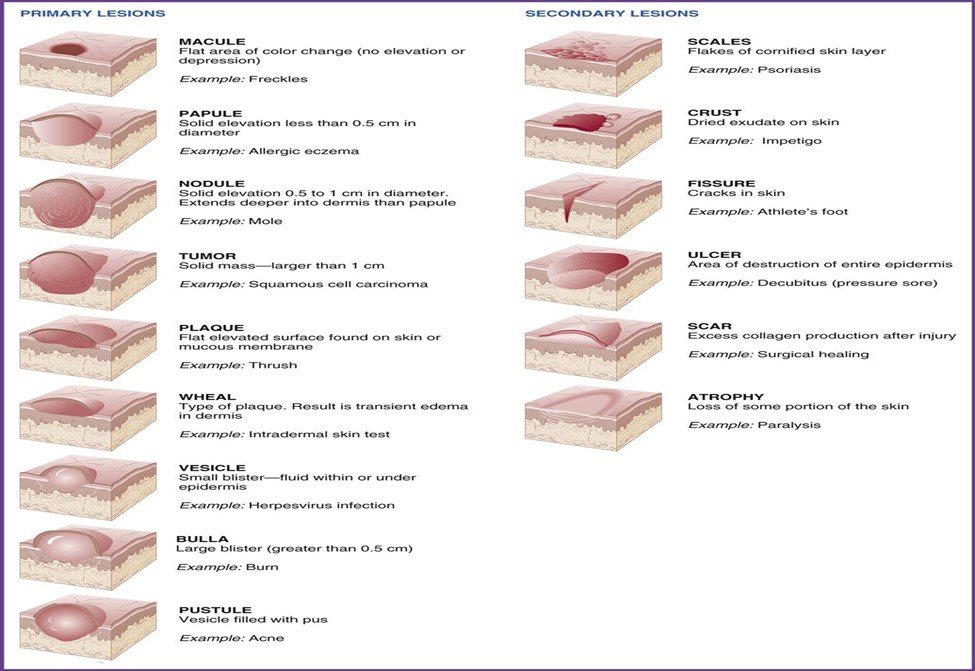
- Vesicles – Small blisters with clear fluid < 10 mm.
- Bulla – Large blisters with clear fluid > 10 mm.
- Cyst – A sac-like structure filled with fluid or semisolid material.
- Fissure – A crack-like opening or slit.
- Erythema – Redness of the skin.
- Nodule – Large elevation in the skin; movable lumps.
- Papule – Small elevation in the skin; movable lumps.
- Polyp – Mushroom-like growth on a slender stalk which protrudes outwards.
- Macule – A flat discoloration of skin.
- Wheals – A swollen, discoloured area of skin.
- Pustule – Elevation containing pus.
- Ulcer – Lesion in the mucous membrane that may lead to bleeding/inflammation.
Symptoms
- Any skin lesions
- Disturbances of skin sensation
- Anesthesia
- Hypoesthesia
- Paresthesia
- Hyperesthesia
- Rashes, possibly with itchiness or pain
- Swellings, lumps or masses
- Discolored skin patches (abnormal pigmentation)
- Dry skin
- Open sores, lesions or ulcers
- Peeling skin
- Red, white or pus-filled bumps
- Scaly or rough skin
Conditions & Diseases
- Dermatitis / Eczema – Inflammation of skin due to allergy to certain foods, drugs or chemicals.
- Cellulitis – Inflammation of skin due to infection.
- Urticaria (Raised wheals) – Severe itching caused by contact with irritants or allergens.
- Alopecia – Loss of hair.
- Petechia – Small pinpoint haemorrhages.
- Wart – Thickening of epidermis due to viral infection.
- Varicella – Viral infection (chickenpox).
- Cyanosis – Bluish/purple discoloration of skin due to lack of oxygen.
- Abrasion – Removal of superficial layer of skin.
- Vitiligo – Irregular milky-white patches surrounded by normally pigmented skin.
- Xeroderma – Excessive dryness of skin.
- Tinea – Group of fungal infections (ringworm).
- Tinea pedis – Athlete's foot: itching, scaling, redness of toes.
- Tinea barbae – Fungal infection of beard area (face & neck).
- Onychomycosis – Fungal infection of nails.
- Albinism – Inability to produce melanin.
- Hematoma – Collection of blood under the skin.
- Pruritus – Itching.
- Lipoma – Benign fatty tumour.
- Herpes simplex – Viral infection due to herpes simplex virus.
- Hyperhidrosis – Excessive sweating.
- Impetigo – Bacterial skin infection causing red sores that break and ooze.
- Psoriasis – Chronic autoimmune disease affecting scalp, face, elbows, genital area, knees, buttocks.
Investigations
- Biopsy
- Laboratory tests
Skin Procedures
- Biopsy – Removal of a piece of skin to be sent to the laboratory.
- Excision – Surgical removal of abnormal growths.
- Repair – Suturing of wounds.